Artificial intelligence (AI) has penetrated various domains of our lives, revolutionizing the way we approach problems and find solutions. Within healthcare, the implications of AI are both transformative and life-saving. AI-based algorithms excel at analyzing colossal datasets, extracting meaningful patterns, and making sense of complex variables. These are all aspects that are particularly essential in the field of cardiology.
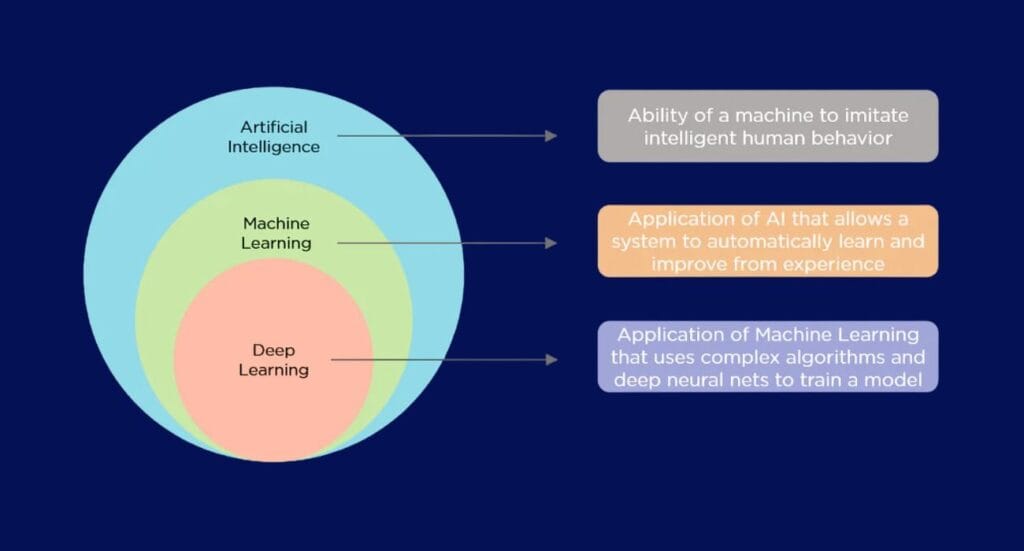
Triad of AI in Cardiology and Healthcare: Machine Learning (ML), AI, and Deep Learning (DL)
In layman’s terms, Artificial Intelligence refers to an array of computational technologies engineered to execute tasks that traditionally require human cognitive functions. This involves a wide range of capabilities, from pattern recognition to decision-making, natural language processing to data or image analytics, and beyond.
Our CMO, Robert Herman, MD, discusses the future roadmap for leveraging AI ECG interpretation on the Mayo Clinic podcast.
As we navigate the technological advancements that are shaping modern medicine, a fundamental grasp of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its various subdomains is crucial.
Distinguishing between Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) can initially appear perplexing due to their intertwined terminologies and concepts, but it’s a necessary step to better understand how AI and its subdomains operate.
Read your next ECG with AI
Be part of a future where cardiac care is smarter, faster, and more accessible. Sign up now and claim your 5 free ECG reports – no credit card needed.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the most general umbrella and serves as an overarching concept that encapsulates technologies fostering intelligent actions in machines. This field includes many diverse technologies that deal with the immense quantities of data, facilitating the identification of underlying patterns within it. The term AI was first coined by John McCarthy in 1956, when he held the first academic conference on the subject.
AI in Cardiology vs Automatisation
The integration of AI in healthcare is often misconstrued as a form of automatization, but the two are inherently different in both intention and function. In this case, Automatization refers to the process of converting tasks based on rule-based algorithms (EX: if X is true, then do Y), traditionally done by humans, into a series of self-executing steps carried out by machinery or software. It aims to enhance efficiency by reducing manual intervention to a minimum, but its rules are all hard set by humans.
Unlike traditional automatization with rule-based algorithms, AI systems “learn” from data, allowing them to make decisions, predict outcomes, and even suggest treatments. The goal is to build systems that can adapt and make decisions autonomously, ultimately aiding—rather than replacing—human capabilities and expertise.
Artificial intelligence in healthcare: opportunities and challenges | Navid Toosi Saidy | TEDxQUT
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning (ML), a specialized branch of AI, concentrates on devising systems capable of learning from data autonomously. The systems evolve to enhance their functionality in specified tasks over time, eliminating the necessity for explicit programming. For example, Algorithms within ML scrutinize data, decipher image patterns, and formulate decisions driven by this analytical process.
Often considered the backbone of AI, machine learning is concerned with developing algorithms that can ‘learn’ from and ‘make decisions’ based on data. The ML model is trained on a dataset, refining its algorithm to improve its performance as it processes more information.
Deep Learning (DL)
Taking the concept of machine learning a step further is Deep Learning (DL), a specialized subset of ML inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, specifically our neural networks. Deep learning algorithms excel at identifying intricate, non-linear patterns in data, which makes them well-suited for functions like image and speech recognition. In the field of cardiology, deep learning can be deployed to analyze a plethora of medical data points, such as ECGs, to provide more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment recommendations.
AI and Cardiology: Match Made in Heaven
The intersection of AI and cardiology is proving to be a revolutionary partnership. Given the data-intensive nature of the cardiovascular field, AI is not merely an optional addition but an essential tool for modern cardiology. The ever-expanding footprint of AI in cardiology enhances the precision and reliability of disease detection from medical images like ECGs, allowing for the identification of complex patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed by human specialists.
1.) Data-Driven Decisions: Enhanced Diagnostics
In the past, cardiology relied primarily on the clinical judgment of healthcare professionals, patient medical records, and the outcomes of diverse tests to make diagnostic and treatment choices. Nevertheless, the field has evolved significantly, encompassing a wider array of cardiovascular diseases and therapeutic alternatives. AI in cardiology now offers a means to address this increasing complexity by providing a supplementary perspective gained from the analysis of vast amounts of data, possibly numbering in the millions. An AI model can complete in mere hours what used to take years of learning and training, occasionally constituting a substantial portion of a person’s career.
2.) Risk Prediction and Stratification through AI
One of the major areas where AI in Cardiology excels is in risk prediction and stratification. Cardiovascular diseases often present subtle symptoms that may not be picked up during routine examinations. AI algorithms can sift through a patient’s medical history, lab results, and other relevant data to identify patterns that are indicative of a higher risk for cardiac events. This predictive capability is invaluable for early intervention and personalized treatment planning.
Can you interpret this ECG?
It’s 11:30 PM, and a 67-year-old male patient presents with two hours of ongoing chest pain. Would you refer for an emergent coronary angiography?
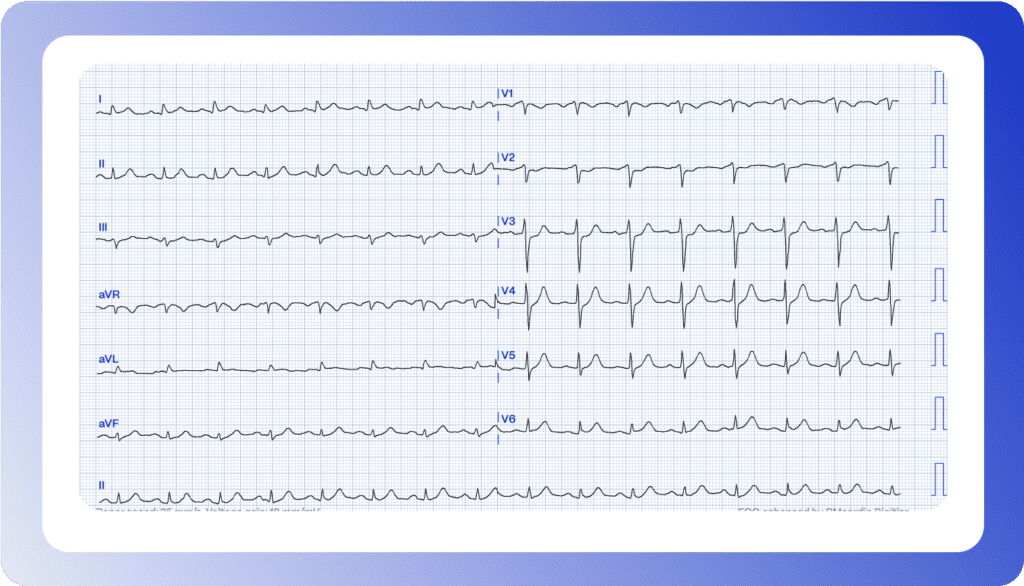
AI-powered ECG Interpretation
The interpretation of Electrocardiograms (ECGs) is one of the most critical aspects of cardiology. Traditionally, cardiologists rely on their skills honed through reviewing thousands of ECG tracings. Enter AI in ECG, capable of processing millions of ECG records within a brief period. Such expansive training enables AI algorithms to identify nuanced patterns and anomalies that even the most experienced cardiologists may overlook.
Unlike humans, who can interpret ECG data based on their training and experience, AI can analyze ECG data against a vast database of clinical outcomes. This ensures a more nuanced and accurate diagnosis, taking into account a range of factors that might be beyond human cognition in a timely manner.
By crunching millions of previous ECGs in a matter of hours, the AI ECG analysis can spot and learn even very subtle patterns possibly missed by the human eye.
Our CMO, Robert Herman, MD, discusses the usage of AI in ECG analysis on the Mayo Clinic podcast.
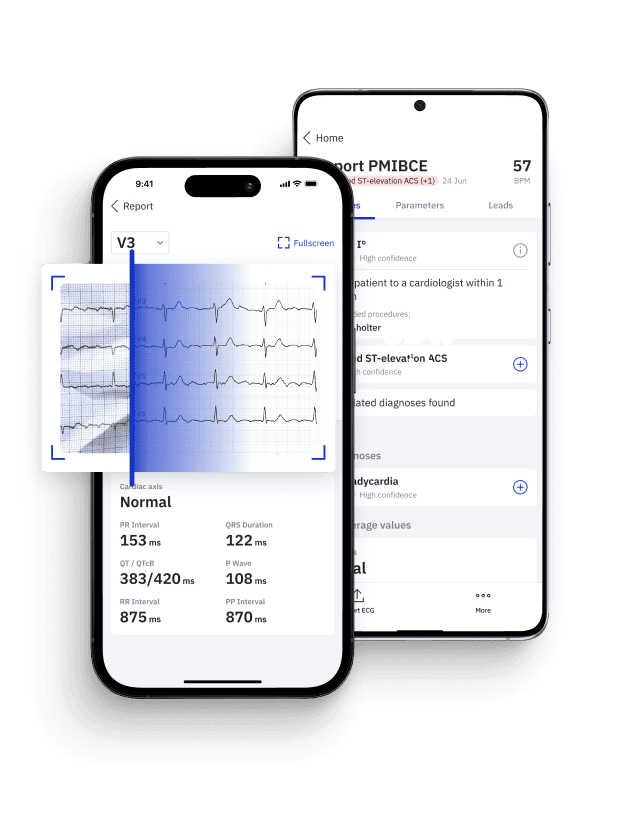
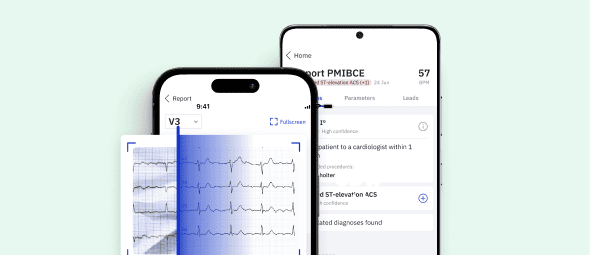
Introducing PMcardio: AI-Powered Precision in Cardiology
As a testament to the transformative potential of AI in Cardiology, PMcardio stands as a remarkable innovation. PMcardio’s AI algorithms are trained on a dataset of one million patient ECGs, which makes them exceptionally proficient in diagnosing 38 different cardiovascular diseases. With a proven track record of outperforming even experienced cardiologists in ECG diagnostics, PMcardio is a powerful tool that healthcare professionals can leverage for quick, accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment recommendations.
PMcardio is designed as a ECG reading app, turning your handheld device into a certified Class IIb medical device capable of digitizing and interpreting any 12-lead ECG in under 5 seconds. Its deep neural network (deep learning algorithm) model has been trained on a total of 931,344 standard 12-lead ECGs from 172,750 patients to detect 38 individual diagnoses including heart rhythms, heart blocks, infarctions, hypertrophies, and ectopies, among others.


Read your next ECG with certified AI
- Diagnose 39 cardiovascular diseases in seconds
- Medical Device Class II(b) EU MDR CE-mark
- 5 free ECG reports - no credit card needed
The Future of AI in Cardiology: The Key is Collaboration, Not Replacement
It’s vital to underscore that the goal of incorporating AI in cardiology is not to replace healthcare professionals but to augment their diagnostic and treatment capabilities. As medical data continues to grow both in volume and complexity, human clinicians can no longer afford to operate in isolation. AI in cardiology offers a collaborative approach, enabling healthcare providers to deliver more precise and effective patient care.
By integrating AI into the existing healthcare infrastructure, the medical community stands to gain immensely in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and patient outcomes. And it is solutions like PMcardio that are leading the charge in transforming cardiovascular care for the better.
The Strengths and Limitations of AI in Medical Data Analysis
AI’s core feature, particularly in Machine Learning (ML) or Deep Learning (DL), is pattern recognition in datasets. This capability is a double-edged sword. On one hand, computers excel at efficiently identifying patterns, which is vital in medicine. On the other hand, substantial data is often needed for accurate modeling, a challenge in medical fields where automated data collection is in its nascent stages. Moreover, ML and DL models struggle with cases they haven’t encountered before, emphasizing the need for reliable and unbiased data sources.
Strategic partnership with the Cardiovascular center in Aalst
It’s here that PMcardio outshined the rest of the competition – a strategic partnership with the Cardiovascular center in Aalst. This collaboration has provided extensive expertise and a significant representative dataset. Furthermore, the development of a sophisticated digitization algorithm capable of converting any image or scan of a 12-lead ECG into a fully digital waveform allowed us to further broaden the spectrum of ECGs to include rare diagnoses that are often only available in non-digital archives, thereby enriching the diversity and comprehensiveness of our dataset.
Concluding Thoughts
The synergistic relationship between AI and healthcare professionals promises to elevate the standard of care, particularly in the realm of cardiology. While AI serves as a powerful tool, the ultimate decision-making authority rests with medical professionals. The coming together of AI and human intellect offers a promising trajectory, one that heralds a new era of medical excellence and life-saving interventions.