Artificial intelligence (AI) is a rapidly growing field of technology with many applications in the healthcare industry. Across disciplines, AI revolutionises how doctors diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases.
In radiology, for example, AI-based image recognition and computer vision technology have significantly improved how specialists detect certain illnesses from medical images such as X-rays or MRIs, as artificial intelligence can recognise complex patterns in imaging data and provide quantitative assessments of radiographic characteristics.
The applications of artificial intelligence in healthcare are numerous, and the number of use cases is still growing. That’s why it’s important for doctors and healthcare professionals to understand what AI is and what it can do.
In this article, you will find all the AI fundamentals explained in the context of healthcare
Table of Contents
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence means the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence to perform.
This includes visual perception and recognition, speech recognition, decision-making, or translation between languages.
Since AI algorithms are typically trained on millions (sometimes billions) of data points coming from medical records or images, this makes them essentially more “experienced” than humans.
Example: ECG interpretation – Human vs AI
So what do we mean when we say ‘artificial intelligence is essentially more experienced than humans’?
Let us demonstrate this on ECG interpretation. A human cardiologist trains his or her skills on several hundred to thousands of ECG tracings. Artificial intelligence, on the other hand, can process millions of ECG records in a matter of days.
For example, this is exactly how PMcardio’s AI algorithms work. Using AI image recognition, the app scans an ECG tracing and reconstructs it into a fully digital waveform.
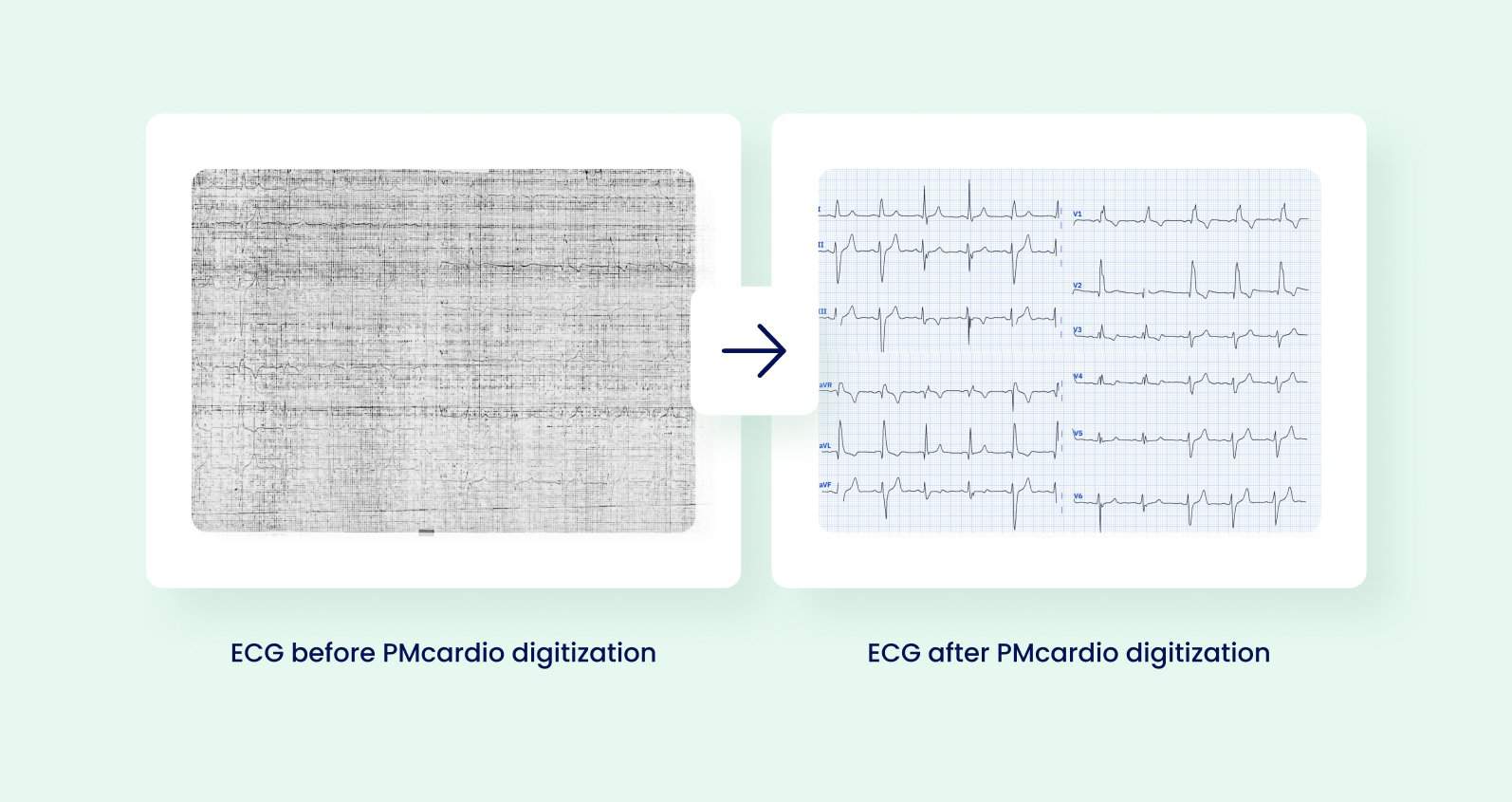
By being trained on a set of one million patient ECGs, PMcardio’s deep learning technology has “learned” patterns and anomalies in ECGs, providing a highly accurate diagnosis of an ECG.
Letting the AI interpret an ECG allows human physicians to get help and a second opinion in making diagnostic and treatment decisions from the machines that have literally “seen” and processed more ECGs than any human physician can.
Since we mentioned deep learning…
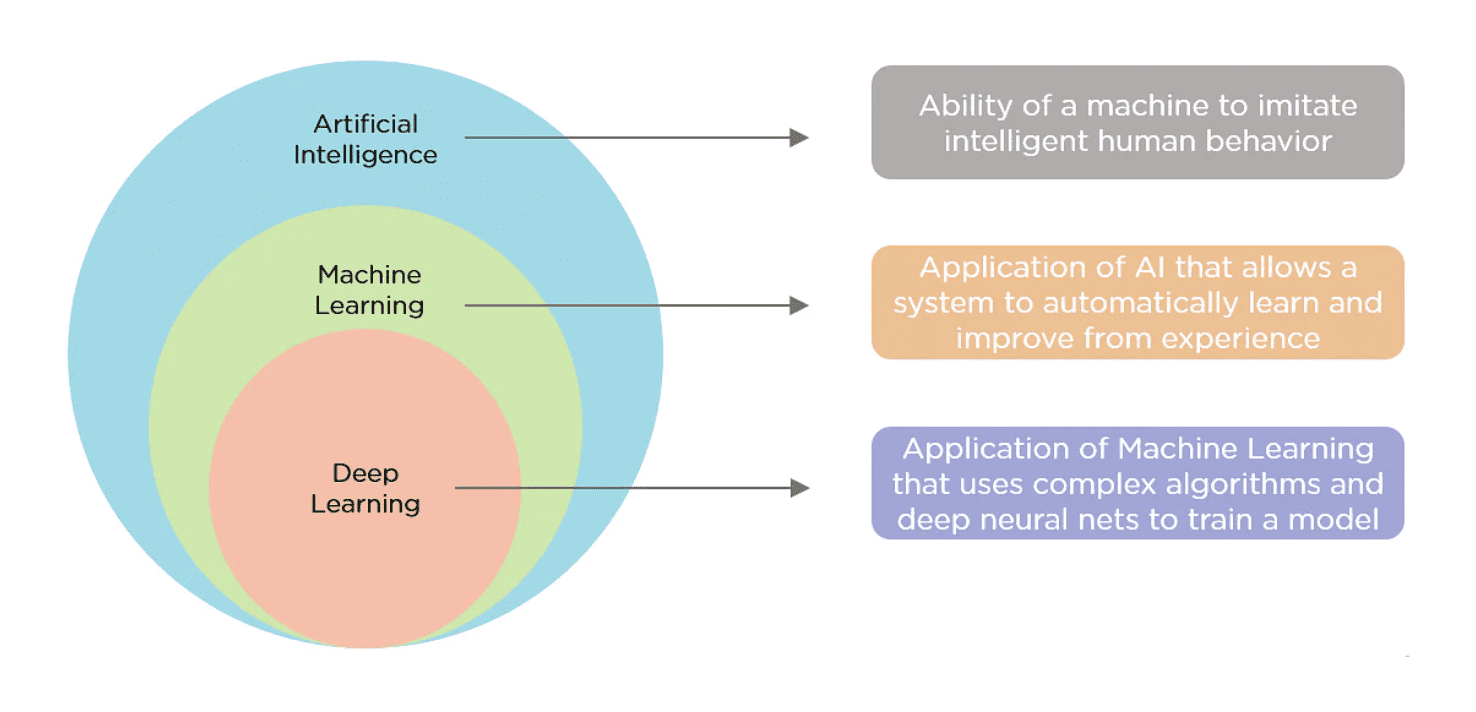
Artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning: What’s the difference?
You may have heard some or all of these terms before, maybe not knowing exactly whether they all mean the same thing or are, in fact, all describing something very different. The short answer is: They’re all algorithm types.
Now, let’s go into more detail.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is an umbrella term for all technology that enables machines to exhibit intelligent behaviour. AI encompasses a wide range of technologies used for processing vast amounts of data and identifying patterns.
Machine learning
Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on building systems that can learn from data. These systems are designed to improve their performance on a particular task over time without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms analyse data, identify patterns, and make decisions based on that analysis.
Deep learning
Deep learning is a type of machine learning that involves training artificial neural networks on large datasets. These neural networks are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, and they can learn to recognise patterns and make decisions based on that learning. Deep learning is beneficial for tasks that require the processing of large amounts of data, such as image and language tasks.
For a better understanding, here’s a visual explanation.
How does artificial intelligence work?
AI algorithms can be trained on data points from past diagnostics, treatments, and procedures that have been successful or unsuccessful.
By having access to such datasets, AI systems can develop a much better understanding of how specific treatments work than if they were just relying on human experience alone. This allows them to make more accurate predictions.
Additionally, as more data is collected over time, these algorithms become more adept at predicting outcomes with greater precision.
For instance, our application PMcardio is built with artificial intelligence trained on 1 million patient cases. Instead of using fiducial points and a set of expert-defined rules, the algorithms are trained on previous patient cases. Feeding the AI this vast amount of data enables the algorithm to identify patterns in the ECGs and, by extension – to learn.
Why is AI important in healthcare?
AI is important in healthcare for a number of reasons.
1/ It can help doctors make more accurate diagnoses by analyzing large amounts of data and identifying patterns that might not be obvious to the human eye. For instance, AI-driven diagnostic tools have been developed to detect certain illnesses from medical images such as X-rays or MRIs with greater accuracy than human experts. This can lead to more effective personalized treatment plans and can help doctors identify potential health problems earlier, which can improve patient outcomes.
2/ AI can help automate many routine tasks in a healthcare organization, such as scheduling appointments, managing electronic medical records, and processing insurance claims. This can free up doctors and other healthcare professionals to focus on more important tasks, such as providing direct patient care.
3/ AI can help improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the healthcare system by reducing the need for expensive and time-consuming tests and procedures.
4/ AI allows doctors to make decisions faster and with greater confidence than ever before. Additionally, since AI algorithms require less manual labour than traditional methods of analysis or diagnosis do, they also help reduce costs while improving the quality of care.
The use of AI has immense potential to improve patient care dramatically.
By leveraging big data and advanced analytics, healthcare professionals will be able to detect illnesses fast while also providing more personalized treatments tailored to each patient’s needs.
Ultimately, this will lead to better patient health outcomes while allowing doctors to spend more time with their patients instead of poring over paperwork and routine tasks.
Will AI Replace Doctors?
As a final thought, AI is definitely not here to replace doctors. No matter how advanced technology becomes—it’s important to remember that doctors are still at the helm when it comes to making decisions about patient care and delivering treatment.
We are strong believers in using the potential of artificial intelligence to help doctors work more efficiently and save lives. We believe that the power of AI lies in its potency to predict certain events better than humans do – for instance, a heart attack or heart failure.
Over to you
As Artificial Intelligence continues to advance exponentially across all industries—including healthcare—it’s essential for medical professionals to understand its capabilities to leverage its power.
Enhance your own practice with Artificial Intelligence and interpret ECGs faster and more confidently with PMcardio.